lv stroke | lv stroke volume normal range lv stroke ¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ . The maximum weight allowed per bag is 23 kg (except for Business Class passengers, whose maximum weight allowance is 32 kg). If you need to, you can increase it from 23 .
0 · stroke volume vs end diastolic
1 · normal stroke volume chart
2 · lvot stroke volume chart
3 · lv stroke volume normal range
4 · lv stroke volume 4c al
5 · lv stroke volume 2d teich
6 · lv stroke volume 1 p
7 · left ventricular stroke volume chart
Rolex Bezel Inserts. We carry a large assortment of genuine Rolex bezel inserts. All are brand new, still sealed in the original Rolex blister packaging. At this time, we only carry .
stroke volume vs end diastolic
The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be reasonable (Class of .¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .
daytona rolex submariner
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of .
eLetters should relate to an article recently published in the journal and are not a .We sought to determine whether an association existed between the .
Assessment of cardiac output (CO) and stroke volume (SV) is important in guiding the . Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) . The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be reasonable (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level of Evidence C-LD). 110 On the basis of consensus opinion, given .
Assessment of cardiac output (CO) and stroke volume (SV) is important in guiding the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic management of a range of cardiopulmonary diseases. CO differentiates low- from high-output heart failure and helps identify low-flow aortic stenosis (AS). Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk. Reduced left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%, a known risk factor for adverse cardiac outcomes and recurrent acute ischemic stroke, may be detected during an acute ischemic stroke hospitalization. The following are key points to remember about this scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) for the management of patients at risk for and with left ventricular (LV) thrombus: Decisions concerning the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of LV thrombus remain challenging.
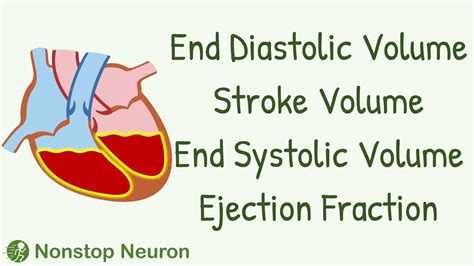
Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method to assess LV function. We also highlight the role of STE in the assessment and management of cardiac and noncardiac disease, including detection of subclinical LV dysfunction. The left ventricular stroke work index (LVSWI) is not a recent development, dating back decades. It is derived from the product of pressure difference (aortic systolic pressure−LV end-diastolic pressure) and stroke volume (SV). 10 As opposed to LVEF, the LVSWI incorporates both LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).Echocardiography (echo) quantified LV stroke volume (SV) is widely used to assess systolic performance after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This study compared two common echo approaches – predicated on flow (Doppler) and linear chamber .
Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction, developed in relation to myocardial dysfunction and remodeling, is documented in 15%-25% of the population. However, its role in functional recovery and recurrent vascular events after acute ischemic stroke has not been thoroughly investigated. The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be reasonable (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level of Evidence C-LD). 110 On the basis of consensus opinion, given .Assessment of cardiac output (CO) and stroke volume (SV) is important in guiding the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic management of a range of cardiopulmonary diseases. CO differentiates low- from high-output heart failure and helps identify low-flow aortic stenosis (AS).
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk. Reduced left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%, a known risk factor for adverse cardiac outcomes and recurrent acute ischemic stroke, may be detected during an acute ischemic stroke hospitalization. The following are key points to remember about this scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) for the management of patients at risk for and with left ventricular (LV) thrombus: Decisions concerning the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of LV thrombus remain challenging.Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method to assess LV function. We also highlight the role of STE in the assessment and management of cardiac and noncardiac disease, including detection of subclinical LV dysfunction.
The left ventricular stroke work index (LVSWI) is not a recent development, dating back decades. It is derived from the product of pressure difference (aortic systolic pressure−LV end-diastolic pressure) and stroke volume (SV). 10 As opposed to LVEF, the LVSWI incorporates both LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).Echocardiography (echo) quantified LV stroke volume (SV) is widely used to assess systolic performance after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This study compared two common echo approaches – predicated on flow (Doppler) and linear chamber .
normal stroke volume chart
lvot stroke volume chart
rolex submariner plastic glass
lv stroke volume normal range

Fake: Fake Dior Air Jordan 1 Low box label has thinner numbers in the barcode. The “3SN268ZDD V00846H1160” text on fake pairs is thinner. The shoe .
lv stroke|lv stroke volume normal range