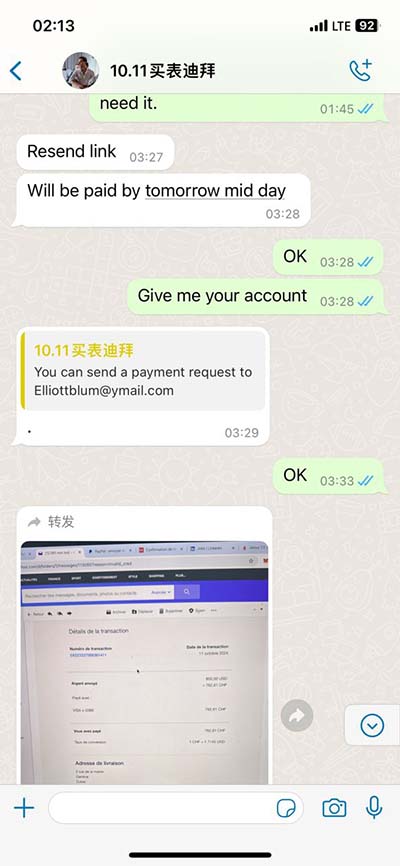
chanel water to surface | surface drainage system diagram chanel water to surface Quasi-steady dynamic-wave approximation. This approximation is often used for water-surface profile computations along a channel reach, given a steady flow. It is incorporated in HEC-RAS. Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the underlying cause. It may include medications, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea, which can .
0 · types of surface water drains
1 · types of surface water drainage
2 · types of surface drainage systems
3 · surface water drainage systems examples
4 · surface water channel offset
5 · surface water channel drainage
6 · surface drainage system diagram
7 · concrete surface water channel
The best part about the Neonoe Bag, though, is the price. Generously sized Louis Vuitton day bags can get very expensive, very quickly, but this one is priced at $1,390. And while that’s not inexpensive, for sure, it’s way less than your average Louis Vuitton bag, and for the price you get a really attractive, functional purse.
This open channel flow calculator will help you find water flow velocity and volumetric flow rate through an open channel, given the channel's roughness coefficient, slope, and cross-sectional area. In this calculator, you will learn how Manning's equation works and how to use it to .
Quasi-steady dynamic-wave approximation. This approximation is often used for water-surface .The standard step method (STM) is a computational technique utilized to estimate one-dimensional surface water profiles in open channels with gradually varied flow under steady state conditions. It uses a combination of the energy, momentum, and continuity equations to determine water depth with a given a friction slope , channel slope , channel geometry, and also a given flow rate. In practice, this technique is widely used through the computer program HEC-RAS, develo.This open channel flow calculator will help you find water flow velocity and volumetric flow rate through an open channel, given the channel's roughness coefficient, slope, and cross-sectional area. In this calculator, you will learn how Manning's equation works and how to use it to determine water flow.
Quasi-steady dynamic-wave approximation. This approximation is often used for water-surface profile computations along a channel reach, given a steady flow. It is incorporated in HEC-RAS.The standard step method (STM) is a computational technique utilized to estimate one-dimensional surface water profiles in open channels with gradually varied flow under steady state conditions.The basic skill and knowledge of how to calculate a water surface profile for an open channel. It’s simply repeating a 2-step process which begins at the downstream end of your system working towards the upstream end.
S = Slope of channel bottom or water surface [L/L]. Vertical distance divided by horizontal distance. V = Average velocity of the water [L/T]. y = Water depth measured normal (perpendicular) to the bottom of the channel [L].Where flowing water water is exposed to the atmosphere, and thus not under pressure, its condition is called open channel flow. Typical design challenges can be: Determining how deep water will flow in a channel. Finding the bottom slope required to carry a defined flow in a channel. The open channel flow calculator can find the water flow rate and volumetric flow rate for custom-sized channels or the most economic cross-sections. In either case, all you have to do is: Begin by selecting the type of design that you'd like to perform. Proceed to enter the slope of the channel s. From the Manning's coeff.INTRODUCTION. A transition is an open-channel flow structure whose purpose is to change the shape or cross-sectional area of the flow. The design objective is to avoid excessive energy losses and to minimize surface waves and other turbulence.
Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow water. The speed or celerity of disturbances in shallow water is given by c = (g Dh) 1/2, where D h is the hydraulic depth. Critical flow occurs when v = c, or more generally1. Assume a water surface elevation at the upstream cross section. 2. Determine corresponding conveyance and velocity head. 3. Compute the friction slope for the reach and then solve for the.This open channel flow calculator will help you find water flow velocity and volumetric flow rate through an open channel, given the channel's roughness coefficient, slope, and cross-sectional area. In this calculator, you will learn how Manning's equation works and how to use it to determine water flow.
Quasi-steady dynamic-wave approximation. This approximation is often used for water-surface profile computations along a channel reach, given a steady flow. It is incorporated in HEC-RAS.
The standard step method (STM) is a computational technique utilized to estimate one-dimensional surface water profiles in open channels with gradually varied flow under steady state conditions.
breitling repetition minutes lugs parts
The basic skill and knowledge of how to calculate a water surface profile for an open channel. It’s simply repeating a 2-step process which begins at the downstream end of your system working towards the upstream end.
S = Slope of channel bottom or water surface [L/L]. Vertical distance divided by horizontal distance. V = Average velocity of the water [L/T]. y = Water depth measured normal (perpendicular) to the bottom of the channel [L].Where flowing water water is exposed to the atmosphere, and thus not under pressure, its condition is called open channel flow. Typical design challenges can be: Determining how deep water will flow in a channel. Finding the bottom slope required to carry a defined flow in a channel. The open channel flow calculator can find the water flow rate and volumetric flow rate for custom-sized channels or the most economic cross-sections. In either case, all you have to do is: Begin by selecting the type of design that you'd like to perform. Proceed to enter the slope of the channel s. From the Manning's coeff.
INTRODUCTION. A transition is an open-channel flow structure whose purpose is to change the shape or cross-sectional area of the flow. The design objective is to avoid excessive energy losses and to minimize surface waves and other turbulence.Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow water. The speed or celerity of disturbances in shallow water is given by c = (g Dh) 1/2, where D h is the hydraulic depth. Critical flow occurs when v = c, or more generally
types of surface water drains
breitling profession 10atm
types of surface water drainage
Region:The Black Shroud; Zone:Central Shroud; Central Shroud Monster; Jadeite Thick Monster; Area:Jadeite Thick; FATE Monster; Central Shroud FATE Monster; Jadeite Thick FATE Monster
chanel water to surface|surface drainage system diagram